Ancient Rome
The Fall of Rome
The Peak of Roman Power
Rome reached its peak of power in the 2nd century around the year 117 AD under the rule of the great Roman emperor Trajan. Virtually all of the coastline along the Mediterranean Sea was part of the Roman Empire. This included Spain, Italy, France, southern Britain, Turkey, Israel, Egypt, and northern Africa.
Gradual Decline
The Fall of Rome didn't happen in a day, it happened over a long period of time. There are a number of reasons why the empire began to fail. Here are some of the causes of the fall of the Roman Empire:
- The politicians and rulers of Rome became more and more corrupt
- Infighting and civil wars within the Empire
- Attacks from barbarian tribes outside of the empire such as the Visigoths, Huns, Franks, and Vandals.
- The Roman army was no longer a dominant force
- The empire became so large it was difficult to govern
In 285 AD, Emperor Diocletian decided that the Roman Empire was too big to manage. He divided the Empire into two parts, the Eastern Roman Empire and the Western Roman Empire. Over the next hundred years or so, Rome would be reunited, split into three parts, and split in two again. Finally, in 395 AD, the empire was split into two for good. The Western Empire was ruled by Rome, the Eastern Empire was ruled by Constantinople.
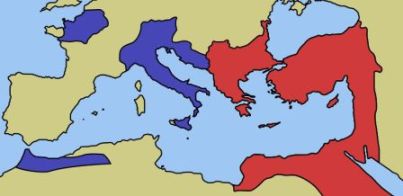
Map of the Eastern and Western Roman Empire right before the fall
by Cthuljew at Wikimedia Commons
The "fall" of Rome discussed here is referring to the Western Roman Empire which was ruled by Rome. The Eastern Roman Empire became known as the Byzantium Empire and remained in power for another 1000 years.
The City of Rome is Sacked
The city of Rome was thought by many to be unconquerable. However, in 410 AD, a Germanic barbarian tribe called the Visigoths invaded the city. They looted the treasures, killed and enslaved many Romans, and destroyed many buildings. This was the first time in 800 years that the city of Rome had been sacked.
Rome Falls
In 476 AD, a Germanic barbarian by the name of Odoacer took control of Rome. He became king of Italy and forced the last emperor of Rome, Romulus Augustulus, to give up his crown. Many historians consider this to be the end of the Roman Empire.
The Dark Ages Begins
With the fall of Rome, many changes occurred throughout Europe. Rome had provided a strong government, education, and culture. Now much of Europe fell into barbarianism. The next 500 years would be known as the Dark Ages of Europe.
Interesting Facts about the Fall of Rome
- The Eastern Roman Empire, or Byzantium, fell in 1453 to the Ottoman Empire.
- Many poor people were glad to see Rome fall. They were starving to death while being taxed heavily by Rome.
- Near the end of the Roman Empire, the city of Rome was no longer the capital. The city of Mediolanum (now Milan) was capital for a while. Later, the capital was moved to Ravenna.
- Rome was sacked once again in 455 AD by Geiseric, King of the Vandals. The Vandals were an Eastern Germanic tribe. The term "vandalism" comes from the Vandals.
- Take a ten question quiz about this page.
- Listen to a recorded reading of this page:
Works Cited